TIP
本文主要是介绍 MapReduce-基本原理和应用 。
# MapReduce-基本原理和应用
# 一:MapReduce模型简介
MapReduce将复杂的、运行于大规模集群上的并行计算过程高度地抽象到了两个函数:Map和Reduce。它采用“分而治之”策略,一个存储在分布式文件系统中的大规模数据集,会被切分成许多独立的分片(split),这些分片可以被多个Map任务并行处理
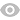
# 1.Map和Reduce函数
Map和Reduce
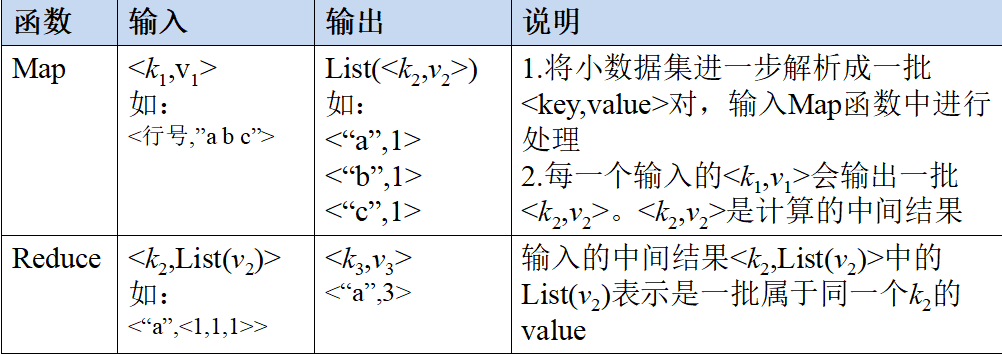
# 2.MapReduce体系结构
MapReduce体系结构主要由四个部分组成,分别是:Client、JobTracker、TaskTracker以及Task
# 1)Client
用户编写的MapReduce程序通过Client提交到JobTracker端 用户可通过Client提供的一些接口查看作业运行状态
# 2)JobTracker
JobTracker负责资源监控和作业调度 JobTracker 监控所有TaskTracker与Job的健康状况,一旦发现失败,就将相应的任务转移到其他节点 JobTracker 会跟踪任务的执行进度、资源使用量等信息,并将这些信息告诉任务调度器(TaskScheduler),而调度器会在资源出现空闲时,
选择合适的任务去使用这些资源
# 3)TaskTracker
TaskTracker 会周期性地通过“心跳”将本节点上资源的使用情况和任务的运行进度汇报给JobTracker,同时接收JobTracker 发送过来的命令并执行相应的操作(如启动新任务、杀死任务等) TaskTracker 使用“slot”等量划分本节点上的资源量(CPU、内存等)。一个Task 获取到
一个slot 后才有机会运行,而Hadoop调度器的作用就是将各个TaskTracker上的空闲slot分配给Task使用。slot 分为Map slot 和Reduce slot 两种,分别供MapTask 和Reduce Task 使用
# 4)Task
Task 分为Map Task 和Reduce Task 两种,均由TaskTracker 启动
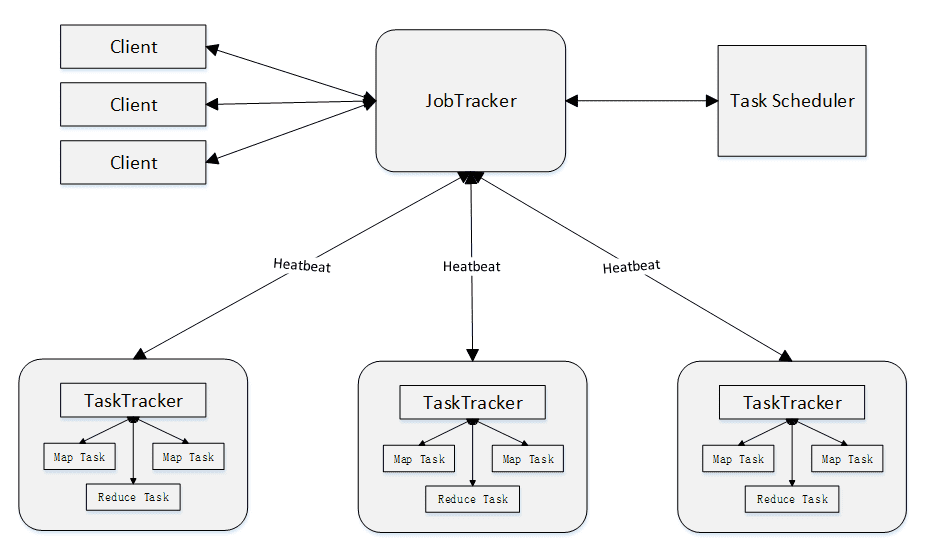
# 3.MapReduce工作流程
# 1) 工作流程概述
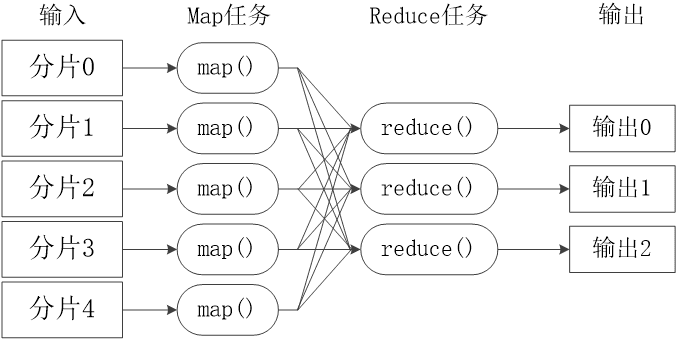
不同的Map任务之间不会进行通信
不同的Reduce任务之间也不会发生任何信息交换
用户不能显式地从一台机器向另一台机器发送消息
所有的数据交换都是通过MapReduce框架自身去实现的
# 2) MapReduce各个执行阶段
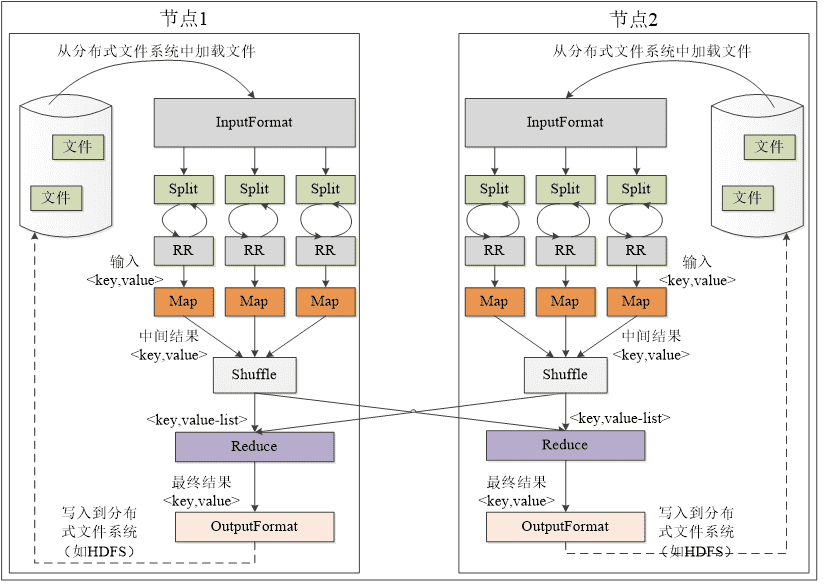
# 4.MapReduce应用程序执行过程
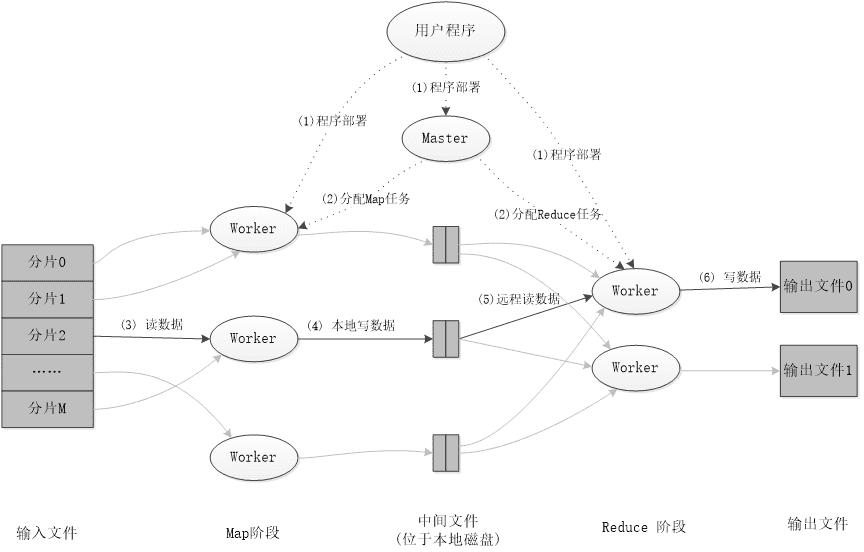
# 二 :WordCount运行实例
工作流程是Input从HDFS里面并行读取文本中的内容,经过MapReduce模型,最终把分析出来的结果用Output封装,持久化到HDFS中
# WordCount的Map过程
1、使用三个Map任务并行读取三行文件中的内容,对读取的单词进行map操作,每个单词都以<key, value>形式生成
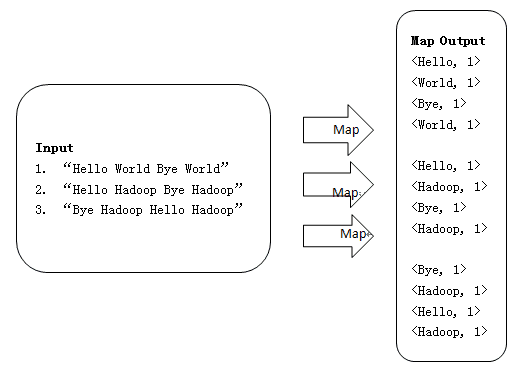
2.Map端源码
public class WordMapper extends
Mapper<Object, Text, Text, IntWritable> {
private final static IntWritable one = new IntWritable(1);
private Text word = new Text();
public void map(Object key, Text value, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String line = value.toString();
StringTokenizer itr = new StringTokenizer(line);
while (itr.hasMoreTokens()) {
word.set(itr.nextToken().toLowerCase());
context.write(word, one);
}
}
}
# WordCount的Reduce过程
1、Reduce操作是对Map的结果进行排序、合并等操作最后得出词频
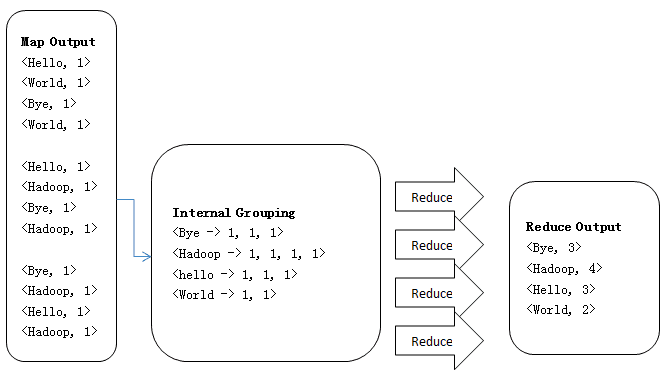
2、Reduce端源码
public class WordReducer extends
Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable> {
private IntWritable result = new IntWritable();
public void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values,
Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
int sum = 0;
for (IntWritable val : values) {
sum += val.get();
}
result.set(sum);
context.write(key, new IntWritable(sum));
}
}
# WordCount源码
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.GenericOptionsParser;
public class WordCount {
public static class WordMapper extends
Mapper<Object, Text, Text, IntWritable> {
private final static IntWritable one = new IntWritable(1);
private Text word = new Text();
public void map(Object key, Text value, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String line = value.toString();
StringTokenizer itr = new StringTokenizer(line);
while (itr.hasMoreTokens()) {
word.set(itr.nextToken().toLowerCase());
context.write(word, one);
}
}
}
public static class WordReducer extends
Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable> {
private IntWritable result = new IntWritable();
public void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values,
Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
int sum = 0;
for (IntWritable val : values) {
sum += val.get();
}
result.set(sum);
context.write(key, new IntWritable(sum));
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
String[] otherArgs = new GenericOptionsParser(conf, args)
.getRemainingArgs();
if (otherArgs.length != 2) {
System.err.println("Usage: wordcount <in> <out>");
System.exit(2);
}
Job job = new Job(conf, "word count");
job.setJarByClass(WordCount.class);
job.setMapperClass(WordMapper.class);
job.setCombinerClass(WordReducer.class);
job.setReducerClass(WordReducer.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(otherArgs[0]));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(otherArgs[1]));
System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1);
}
}
# 参考文章
- https://www.cnblogs.com/lixiansheng/p/8942370.html